Okay, now that’s something that can’t be ignored. Can it? I doubt that since your emails don’t reach the inbox then who is ever going to read them?
Do people check their spam mails ??
Umm, I really don’t think so.
So this is a problem faced by a lot of startups mostly since they do not have any sender score built up for their domain. The struggle with the delivery across different mailbox providers is a set-off.
Few senders also struggle with the delivery problem as well as the engagement with the customers through one mailbox providers. There are spammers who get hold of the list and take over the messages from the new IPs/Domains and then vanish.
Let’s talk about how to optimize the deliverability of the emails. To make sure your email reaches the inbox rather than the spam.
How to optimize your email sender reputation:
- It’s important to make sure you are sending the email to the right person, i.e the people who have subscribed for it.
- All the invalid email addresses are removed.
- The content should be relevant and should have meaningful information in the Subject, From, and Reply-to headers.
- Take care of all the unsubscribed requests, spam complaints, and users who are not active with your email, i.e no click within 30 days.
- The suppression list should be maintained and in case of any form of migration from a specific company it should be taken along.
- DKIM should be set up and verified for your Domain.
- Set up a Custom Bounce Domain.
- Set up a Custom Tracking Domain.
It is very important to build a sender score with the Email provider. Without this, it is really difficult to optimize your email deliverability.
In this case, let’s avoid these bad practices:
- Sending the message without testing it.
- Use a misleading subject line.
- Hide the sender and unsubscribe link.
- Obtain the email list from an unreliable source and sharing it with the third party.
- Ignoring the unsubscribe request.
- Email appending should be avoided.
It is important to have the consent of the recipient prior to sending messages to an Email address. This consent also involves adding the recipient to any ongoing and repeated communications. This gives a chance of not having emails considered as unwanted or abusive.
The subscription can be at different levels
1. Single opt-in
This is for extreme situations as it means adding an unconfirmed address to the mailing list. There is a possible chance of emails going unchecked, unsubscribing, and eventually the decline in the sender’s reputation.
The recipient should be aware of the fact about receiving the email notification when the address is being collected.
The sender should also specify the listed recipient wants to be included. For example, do they want to receive an email notification regarding the product they have purchased or a similar one? This kind of control helps the senders to send more efficient emails reducing the chance of emails going unchecked.
Email addresses should be used only got the purposes disclosed to the recipient at the time of signup. The email can have a visual example making it more likely for the recipient to view it.
2. Double opt-in
The email subscription under this confirms his or her wish to be added to the mailing list twice. The confirmation consist of two steps –
- The contact fills out the form
- The contact gets a confirmation email along with a link to confirm
- They are now added to your list along with information on their IP address and when they sign up and subscription confirmation.

3. Single opt-in with notification
A confirmation email is sent after they sign up. The email here should include the same “From” address so as it allows the recipient to add it to their address book.
The server sending confirmation emails should be differentiated from the bulk sending IPS.
4. Confirmed opt-in
Recipient of the confirmation messages requires taking an action so as to be added to the list. The confirmation email should be free of advertising as to avoid it being considered as abusive emails.
Sometimes, an email gets a better response if, during the collection of the address, the consent of the customer regarding the notifications of the emails and being added in the mail list is taken into consideration.
Unsubscribe
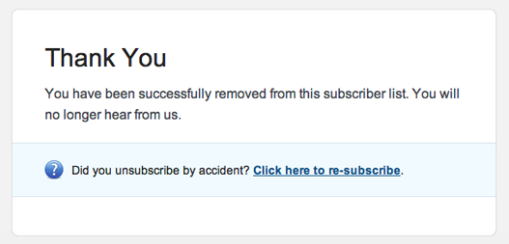
It should be easy, clear, and should be done instantly as a request is received. The longer the request is delayed it is considered as email abusive and complains.
The Unsubscription link should have a subscription ID and a list to unsubscribe from in case of multiple lists.
Senders should use an easily readable text description instead of images, to accompany hyperlinks a click online unsubscribe webpage. Senders should be capable enough to process email-based unsubscribe requests through forms and replying to address in the unbound emails.
Senders should also a policy for unsubscriptions. It will be different for various businesses but they have to decide if the unsubscribe should be valid for all emails or an individual list. It is better to remove the recipient from the entire list. The offline unsubscription option should be available.
When a hyperlink is presented with an online subscription that includes multiple subscription options, the option to unsubscribe should be available on the entire list. The returning subscribers should be made available with the new selections unchecked by default.
It should be made easy for the subscribers to unsubscribe without any hassle or experience any other form of security. A recipient email address should be included in the message body to remind the recipient of the email address they have used to subscribe to a particular list. This is required in case the recipients have multiple email addresses.
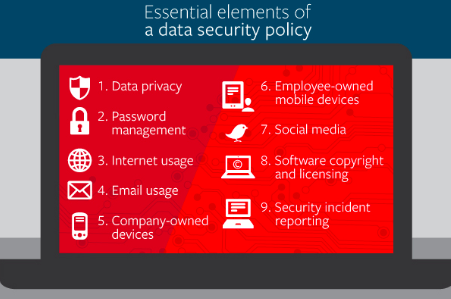
Data security
Security is one of the primary considerations to be taken into notice. Cybercriminals have the tendency to obtain an email address for the wrong reasons. Since software applications store only email addresses it should not be seen as though it can’t be attacked by cybercriminals. This data can be misused, so it is important to in-store this data appropriately.
Data Transparency
It is a form of principle required for building trust in the email industry and also includes IP and Domains of the senders along with any links that might be included in the message body of the email. So this way senders have held all the responsibility for any kind of happening. With transparency, senders build trust and the ability to deliver the emails to the inbox while keeping away from spam.
Receivers can know all the information about senders through the following mechanism –
WHOIS Information:
This helps get the contact information for the IP address or Domain name administrators. It is important for the senders to maintain up to date WHOIS information. It is important for the senders to provide appropriate points of contact to help remedy abuse related issues.

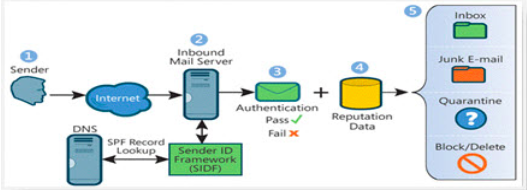
Email Authentication:
This form of authentication further helps to clear out the identity of the sender thereby, avoiding any kind of forged or abusive email address. With a proper authentication and identity clarification, the receiver can make an easy decision based on the mailing history and reputation for a Domain.
There are other ways as well to detect the authentication of the sender’s/ Domain.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework) – It is required to detect email spoofing, and validate the sending IP and HELO domain.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) – It uses a digital cryptographic signature to validate a specific domain in the headers.
- DMARC ( Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) – This gives senders to control as to where is their authenticated and unauthenticated emails with their domain are being delivered. It also helps to set policy for the emails that do not get through the SPF and DKIM.
IP details
This provides guidelines for the transparency of the sender and to know their responsibility of sending mails server to the system making their filtering decisions. These guidelines also help during any complaint or issue.
The guidelines are:
DNS Forward –
It is required to find a domain name using an IP address. A name must be given to identify the responsible party’s domain. The name should indicate that the machine is a server.
In the case of shared IP, there can be more than one name pointing at the same IP address.
Whereas in the case of dedicated IP situation all the emails belonging to an advertisement/ESP required for sending emails should use the same name or a small number of names at the domain registry level and different subdomains can be used.
Example: Do not use espname01.com, Instead use server1.espname.com, etc.
Reserve DNS –
It is used to find a domain name using an IP address. This is also called as PTR or IN-ADDR configured. One IP address should be used in the case of one reserve DNS and the name should match the primary name.
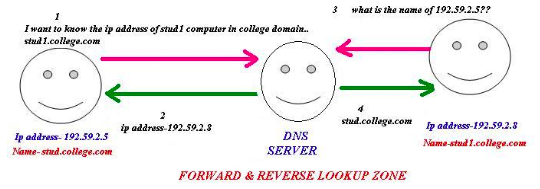
HELO names –
It is identical to the full hostname of the mail server. It is required in SPF authentication. The HELO should be matching the DNS name.
It can sometimes be useful in diagnosing email problems with NATs. So each mailing system or customer in a shared environment behind NATs should have their own HELO name which is the subdomain.
IP environment – (shared and dedicated)
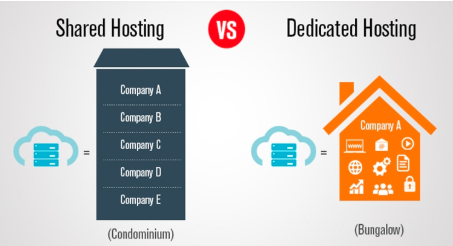
Dedicated environment:
The sender or ESP may want to isolate the emails from other entities, to protect the reputation, develop quality emails, and also track the quality.
The sender can also control the number of emails originating with an IP. A combination of marketing and transactional email or mail of other categories can create an irregular traffic volume. The consistency of the volume describes an integral part in determining the IP reputation and deliverability.
The entity may require an outbound MTA setting that is different from the shared environment. The entity may also require certification, whitelisting, or enhanced deliverability service from a third party.
Shared environment:
The mails from more than one entity can be combined to have a consistent average sending volume to establish and maintain IP reputation. By provisioning the number of entities within a shared environment, a mistake made by a single sender can affect the entire reputation of the IP.
This is comparatively less expensive and makes the mailing system feasible for small businesses.
Vetting –

All the ESP must have a vetting system since it helps to determine between the spammers and a customer. Vetting of clients is an integral part of maintaining a good reputation and decreasing messaging abuse.
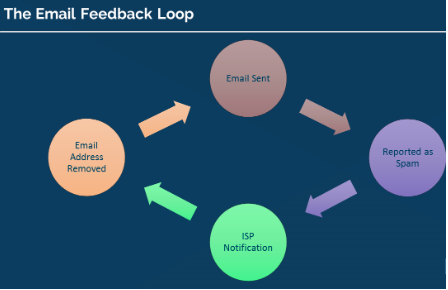
Feedback Loops –
This is the largest source of complaint data senders receive from automated feedback loops which are needed to be set up by the mailbox providers, but ESPs can also receive complaints directly in the mailbox. ESPs should be able to handle complaints received. Complaints help to determine whether the email sender is not in any way violating the terms and conditions.
Forwarding Service –
The ESP may be set up for small customers with an address based on the ESP sending domain for the use in the header of their message. The ESP may be required to forward the replies to the customer, for this ESPN set up a mail forwarding service.
Non-deliverable handling –
There may be a possibility that the email sent may not reach the customer even with the correct address. The reason being the email system may reject or return the emails to the sending system.
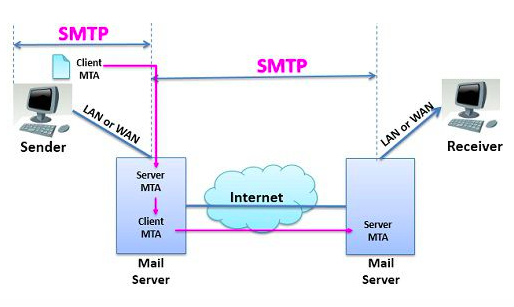
The sender needs to make sure that they have sufficient resources for sending and receiving volumes of SMTP traffic.
When a sender receives an email return it may be rejected in the SMTP conversation. This can happen hours or days later as well. There is about 95% of returns that occur. The sender should identify the address which has bounced the email in order to process them correctly.
The reason can consist of numeric “status code” and a “descriptive message”. Most MTA software, ISPs, and mailbox providers will provide an honest and accurate “status code” that follows the RFC requirements.
Understanding and adjusting to the multitude of receivers returned messages is the key required to get your mail accepted and maintain a reputation.
Permanent failures –
This indicated the message should not be retried to send. This is most common in “users unknown”. Many types of 5xx codes indicate the policy violation as per the descriptive text. These types of errors do not allow the sender to retry sending this message.
It is important to take into account your sending reputation in the past and present. Sometimes the emails delivered to the inbox get marked as junk and this is because the message sent is of poor quality. So the goal of ISPs is to make sure recipients do not get any spam messages, so therefore they go through every information to avoid this.
The sender should make it a point to take into consideration the preferences and the expectations of the recipient. The sender should obviously follow all the policies and guidelines and if required should follow up with their legal department on the choices made to ensure they are in compile with the law.
In the case of new contacts, senders care more about the relationship they share with the customers. The more contacts open your message from you, the more it will create a form of good behavior.
Generally, reputable senders have a list of customer base they send emails to. But in case of a new contact, it won’t work right away. To figure this out, try to separate your transactional message from marketing messages. But in case your email only contains welcome messages to first-time customers, try to min other types of transactional messages like confirmation, password reset, etc. This will help even out first time recipients.
When an email is sent it can be marked as junk by the recipient. This is to be taken into consideration as to how many of these emails land into junk, in order to add value to your email campaign. Keeping a track of email can provide great insight into user behavior. So, be mindful and try to make adjustments in your mail stream.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How to stop emails going to the spam folder?
When you do unwanted email activity such as sending cold emails to more than 80 emails a day and nobody responds but for days but you keep sending an email. That’s how your email gets marked spam. There are many more factors that play role in this.
Why my personal emails are going to spam?
All emails get the same treatment from mail providers such as Gmail, Yahoo, AOL, etc. If the engagement rate is really low on your email then mail providers consider it as spam.
How to remove email id from the spam list in Gmail / Yahoo/ Hotmail?
It takes time. It won’t recover automatically. You need to ask your colleagues, clients, or friends to start email conversations with you and you need to reply to them. It takes 2-3 months to build the same trust again with mail providers that you’re a real person and you do not send spam emails to people.
About the author
Co-Founder @ BigRadar. Building conversational interfaces for small and large enterprises.
- Sandeephttps://bigradar.io/blog/author/sandeep/
- Sandeephttps://bigradar.io/blog/author/sandeep/
- Sandeephttps://bigradar.io/blog/author/sandeep/
- Sandeephttps://bigradar.io/blog/author/sandeep/
![Featured image for blog post Optimize Your Website For Lead Generation [2023]](https://bigradar.io/content/uploads/2023/02/Increase-Your-Website-Traffic-Conversion-300x200.png)
8 thoughts on “How To Send Emails To Inbox Not Spam?”
Nice Blog with good information
Nice Blog with good information
Insightful information about email outreach.
But, still the emails are landing in Junk/ Spam folder? Do i need to change the domain?
Appreciate your help
Hi Elviz,
There might be plenty of reasons:
– You might have sent too many emails.
– Your email content might be spammy.
– You might have sent an email to large audience without personalizing the email.
Quick solution: Change the domain, and warm-up your emails before sending it to a large audience.
Insightful information about email outreach.
But, still the emails are landing in Junk/ Spam folder? Do i need to change the domain?
Appreciate your help
Hi Elviz,
There might be plenty of reasons:
– You might have sent too many emails.
– Your email content might be spammy.
– You might have sent an email to large audience without personalizing the email.
Quick solution: Change the domain, and warm-up your emails before sending it to a large audience.
thanks for the post. Can you also help in this.
how to stop emails from going to spam gmail?
It has been 2 months but nothing is helping out. my official email id is delivering emails in spam folder which is really affecting my business reputation.
i tried the following:
– Asking few friends to mark as not spam.
– stopped sending emails, new composes.
– Applied DKIM, SPF records etc.
would really appreciate your help in this.
thanks for the post. Can you also help in this.
how to stop emails from going to spam gmail?
It has been 2 months but nothing is helping out. my official email id is delivering emails in spam folder which is really affecting my business reputation.
i tried the following:
– Asking few friends to mark as not spam.
– stopped sending emails, new composes.
– Applied DKIM, SPF records etc.
would really appreciate your help in this.